EXCLUSIVE Tesla in talks with Baidu Apollo, explores robotaxi launch in China, sources say
Tesla and Baidu Apollo hold exploratory talks regarding the robotaxi service launch in China and the robocar alliance, two sources familiar with the matter told CarNewsChina.
“They (Tesla) will most likely not get the permit to transfer data collected by their fleet needed for FSD training out of China to the US. Their plan B is to co-store and locally process data with us as we already have mapping license cooperation and experience with our own robotaxi service,” the person who remains anonymous as he is not authorized to talk with the media told CNC.
Tesla and Baidu, also called China’s Google, are not strangers. The two giants began their partnership in early 2020, and Tesla has already integrated Baidu’s navigation map into its vehicles in China. Last week, on April 28, it was also reported that Baidu struck a deal with Tesla to license its mapping service for data collection, paving the way to launch the FSD in China.
The report concluded Elon Musk’s short trip to China, where he met with Chinese Premier Li Qiang. Musk previously announced that Tesla is now fully focused on the launch of a fully autonomous robotaxi service and will make a major announcement on May 8. The source told CNC that Tesla seeks to launch a fully autonomous robotaxi in China before the US.
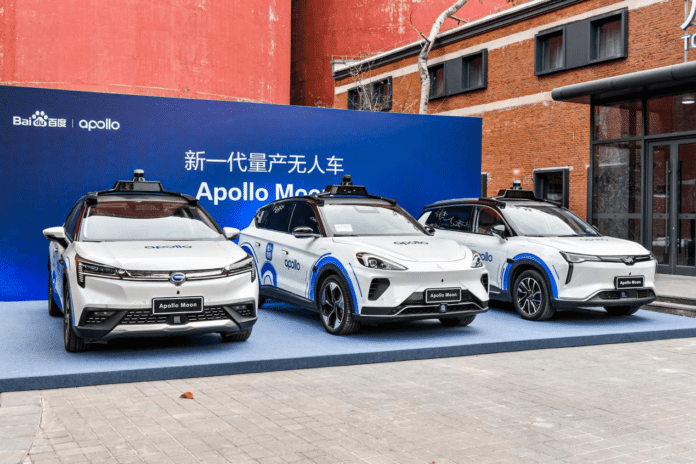
Baidu Apollo is Baidu’s self-driving project focusing on level 4 (L4) autonomous driving. On February 26, Baidu received the permit to offer robotaxi service at Daixing Airport in Beijing. On March 8, the company launched China’s first 24/7 fully driverless robotaxi service in Wuhan.
With the approval granted by the head office of the Beijing High-Level Automated Driving Demonstration Area, Apollo Go can provide autonomous vehicles on the 40-kilometer expressway connecting Daxing International Airport and Beijing urban areas.
In addition to Beijing, Baidu’s fully autonomous driving robotaxis already operates in several cities nationwide, including Chongqing, Wuhan, and Shenzhen.
Baidu claims Apollo Go is the world’s largest autonomous driving mobility service provider. As of September 30, 2023, it had accumulated more than 4.1 million ride orders. In the Q3 of last year, Apollo Go provided 821,000 rides, marking a 73 percent surge compared with the previous year.
Baidu is also the first company in China to get a permit for testing driverless buses on public roads. In 2022, it unveiled the Baidu RT6 Robotaxi fully autonomous concept car, which CarnewsChina had an exclusive first look at.
Despite the Apollo Go progress, Baidu lacks customers for its self-driving solution. The only one so far is Jiyue Auto, which launched its Robo-01, later renamed Jiuye 01, and recently unveiled the Jiuye 07 sedan at the Beijing Auto Show. However, Jiuye is a joint venture between Baidu and Geely.
Baidu Apollo faces tough competition from other Chinese autonomous driving companies like WeRide, Pony.ai, and AutoX. Moreover, EV startups are developing their own solutions, such as XNGP from Xpeng, NOP+ from Nio, NZP from Zeekr, or ADS from Huawei. Partnership with a US EV giant might be a needed cheer-up for Baidu’s AV effort.
No data outside China
Data security and regulatory compliance concerns have been significant hurdles for Tesla, which introduced its Autopilot software four years ago in China. However, despite strong customer demand, FSD is unavailable in the country.
Since 2021, Chinese authorities have mandated that Tesla store all data gathered by its vehicles in China within the country, preventing the company from transferring any of this data back to the United States.
Reports indicate that Musk wants approval to transfer the data collected from Tesla’s vehicles overseas to China. This data would be used to train algorithms for autonomous driving technologies.